The Role of Universities and Research Institutes in the Digital Transformation of the Economy towards Smart Cities Development in Vietnam (Part 2)
28 February, 2022
The roles of the Party-State, enterprises and universities, research institutes towards the digital transformation of the economy in Vietnam
The role of the Party – State and that of enterprises
Digital transformation of the economy is a continuous process that requires the participation of diverse actors in society. To successfully implement the digital transformation of the economy and towards building a smart city, proper identification of the roles of the participants is a prerequisite. In Vietnam, the fact that the leadership, direction and management role of the Party and State in the digital transformation is irreplaceable has been reflected in strategies, policies, decrees and action plans. Specifically, the Politburo issued Resolution 52-NQ/TW on a number of guidelines and policies of Vietnam in participating in Industry 4.0 (Nguyen, 2019). The resolution clearly shows a positive view in renewing thinking, unifying awareness, strengthening the leadership role of the Party and the management of the State. This is the premise for the birth of the National Digital Transformation Program with the goal of developing digital government, digital economy, digital society and forming digital technology businesses (TechPort, 2018). From this Program in combination with the Project of Building Ho Chi Minh City into a Smart City (University, 2019), the Digital Transformation Program has been announced by the People’s Committee of Ho Chi Minh City, featuring the mindset of accepting new things and factors. Institutions, awareness and policies are totally important besides technology (TopDev, 2020). In addition to the role of the Party and the State, businesses operating in the field of information technology (IT) are identified as playing a central role in leading and creating breakthroughs in design and supply as well as providing a digital platform to serve the needs of digital transformation. In Ho Chi Minh City, digital enterprises account for about 3% of the total number of businesses operating in the city; in innovative start-ups, up to 70% of enterprises are in the IT field; Labor productivity in the IT sector is 1.96% higher than that of the city’s overall labor productivity, contributing 4.44% to the city’s domestic product (Pwc, 2018). According to Directive No. 01/CT-TTg of the Prime Minister on promoting the digital technology enterprise development in Vietnam, by 2030, Vietnam needs at least 100,000 digital technology enterprises to carry out the digital transformation mission, digital economy development, smart city building and sustainable development (Grajek, 2020).
The role of higher education institutions
In addition to the Party – State and business entities mentioned above, higher education institutions are important actors in the innovation ecosystem, digital transformation of the economy and towards building a smart city. According to Resolution 52-NQ/TW on a number of undertakings and policies of Vietnam in participating in Industry 4.0 (Nguyen, 2019), the national innovation system is developed in the direction of enterprise-centered Centers, universities and research institutes are strong research subjects. In the National Digital Transformation Program (TechPort, 2018), the role of higher education institutions only stops at education and training and provides high-quality human resources according to occupations associated with digital technology and proactive human resources on demand.
High-knowledge resources are concentrated in universities and research institutes. Currently, these highly knowledgeable resources are taking on the role of research, implementation and consulting in various projects in the field of digital transformation, smart city development with the position of experts, implementation and so on but mainly is as an individual. The advisory and decision-supporting role of universities and research institutes has not been adequately addressed. Not many projects, actual research has the participation of representatives from schools, research institutes or brought back to universities and research institutes to implement in conjunction with stakeholders. Many prestigious universities and research institutes have established professional councils that can fully undertake consulting on related projects. The absence of representatives of universities and research institutes in specialized fields in consulting and decision-making of development strategies and project implementation will reduce the integration between science and reality as well as affect the effectiveness of the project.
Besides, data collection mostly only serves for each specific research need, project or activity carried out in each individual enterprise, organization or unit. If necessary, it will be necessary to carry out the work of seeking, “ask” and “give” in each context. The integration, management and use of common data to serve research projects to solve urban or community problems have not been formalized and are truly open to sharing. If the database continues to collect and store a single, low-accessibility as it is today, it will be difficult to have timely analysis, plans, forecasts and decision-making to meet the development requirements that are growing fast and high in the digital era. Moreover, the researches of universities and research institutes are carried out from highly intellectual human resources; therefore, they need to be utilized to have effective solutions for the society and as the social responsibility that the universities and research institutes are currently doing. It is necessary to have a large and integrated source of data to share for research in the system of universities/research institutes in each field.
CSIRO, 2019 has pointed out four components and roles of parties when participating in the digital economy, including businesses, individuals, policy makers, innovation actors (universities and research institutes). However, the role of universities and research institutes in Vietnam in the digital transformation process has only focused on creating innovations for the digital economy, training and fostering talents, and increasing the number of students. strengthen cooperation and create an innovation community as a driving force for the economy. The role of participation as a representative in consulting, research and decision-making like developed countries has not been mentioned and does not seem to be completely concerned at present.
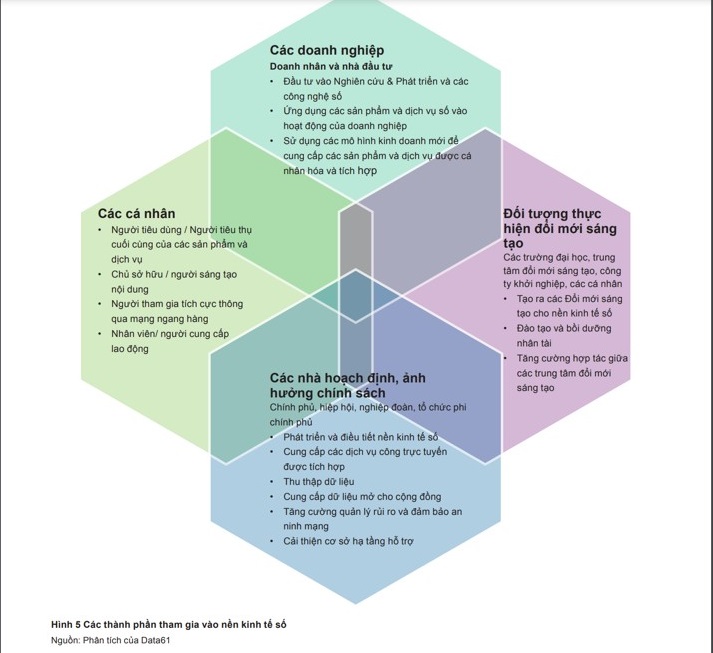
Components participating in the digital economy (CSIRO, 2019)
Quite a few universities in Vietnam have begun to accelerate the process of digital transformation in education to realize the goal of educating and training high-quality human resources in occupations associated with digital technology and key human resources. moving in the digital age. Hanoi University of Science and Technology also has a digital transformation strategy and identifies 4 main technology platforms including Cloud Computing, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things to restructure services and products, creating a breakthrough in the higher education experience environment; at the same time, optimizing the current system and process (Hanh, 2020). As part of the digital transformation strategy to add value to the community, towards a smart and sustainable city, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City has focused on building digital transformation in infrastructure, education and so on. Typically developing a smart library with integration in management – service – experience – smart infrastructure to personalize library user experience: this library serves not only pupils, students, doctoral students but also the community (UEH, 2020).
A limited number of universities have started multidisciplinary integration activities, developed in research to solve urban problems, being ready to participate in consulting, implementing digital transformation projects, smart cities with as a participant as development models in countries around the world. For example, University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City (UEH) established an innovation institute, an institute of smart cities and management and so on pioneering in developing incubators for startups, providing knowledge. on innovation, creativity, and development of the smart city studio-lab system and so on in order to cooperate with stakeholders to solve urban problems in the direction of smart city development and sustainability, being ready to perform the role new digital era and following the general development trend of the world.

UEH Institute of Smart Cities and Management (ISCM) applying VR virtual reality in UEH events
Proposing solutions towards smart cities in Vietnam
The role of providing high-quality and practical human resources
Through the above analysis, it can be recognized that the Industrial Revolution 4.0 creates a strong change in the labor structure; thereby, having a strong impact on education and training of human resources. Ordinary occupations will be gradually replaced while new jobs will arise; however, totally high requirements will be placed on labor qualifications with diverse new and more complex skills with more rapid changes. Therefore, human resource training is facing the heavy pressure of change. For a university, two products of human resource training in the digital era are employees and experts.
Outputs are employees: in addition to being equipped with professional knowledge, they need to be fully equipped with necessary digital skills to adapt to Industrial Revolution 4.0. Basically, these digital skills include skills in using computers and the Internet in addition to self-study skills to improve daily digital skills, to avoid falling behind in the digital age. Studies also show that inequality in digital access (digital inequality) will deepen social inequality. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure digital access to necessary digital skills for everyone, especially for a country with different conditions for accessing technology in different regions, especially limitations in the highlands and deep regions.
The primary product is experts, who are pioneers in the study of new knowledge, skills, and technologies, as inputs to research and development roles.
The role of Research and development (R&D) role
Currently, research and development has been strongly developed in universities, especially universities associated with academic research. However, this activity mostly stops at a few individual experts in the fields. In the process of digital transformation, together with governments, businesses, individuals and universities can promote their role as a continuous research and development center towards improving efficiency and reducing production costs in terms of the organization, not only at the individual experts under the university. To fulfill this role, it is necessary to have financial support from domestic and foreign units that need to solve problems for their units or solve urban problems. Build a living lab system like that of developed countries.
The role of consultant and participation in the decision-making team
In addition to university-affiliated research and development centers, simulation labs and living labs are becoming increasingly common at universities. This is the place to help policy makers and decision-makers make informed decisions and minimize risks.
In addition, the trend of applying big data in fields listed as transportation, E-government, and healthcare is increasingly popular; nevertheless, this trend is only confined to specialized units in each field, without the connection between sectors together to create a whole national data, is the core foundation for effective decision making. More than anyone else, the university can now be a place to store, integrate, exploit and use the national data warehouse, serving research and development (R&D) and providing information towards the authorities’ decision making.
The role of connecting and promoting generations’ participation
One of the factors that determines the success of the digital transformation process in an economy is the understanding and the participation of all generations and classes in one society. With the advantage of being an educational institution, not for commercial purposes, universities play a reasonable role in connecting generations (pupils, students, graduate students, alumni and so on) to participate in this process.
In order to successfully and effectively implement the digital transformation of the economy as well as develop smart cities in Vietnam, it is necessary to integrate industries, fields, stakeholders, levels, sectors and the role of universities and research institutes beyond educational mission in research, consultation and decision support should be strengthened.
Author group: Dr. Trịnh Tú Anh, Ph.D Student Phạm Nguyễn Hoài, Ph.D Student Lê Thị Hạnh An (UEH Institute of Smart City and Management ISCM – School of Technology and Design).
This article is in series spreading researches and applied knowledge from UEH with “Research Contribution For All – Nghiên Cứu Vì Cộng Đồng” message for 2022 period, UEH would like to invite all dear readers to look forward to Newsletter ECOCONOMY #30 “Law amendment to meet the requirement of personal data protection in Digital Transformation”.
Please refer to [Podcast] The Role of Universities and Research Institutes in the Digital Transformation of the Economy towards Smart Cities Development in Vietnam (Part 1) here
News, photos: Author group, UEH Department of Marketing – Communication